toLowerCase Locale toUperCase Locale Java Android
String s = "AbcČ";
String s2 = s.toLowerCase(new Locale("cs_CZ")); // Czech Republic
String s3 = s.toLowerCase(new Locale("de_DE")); // Germany
//
en_US
en_GB
ar_EG
be_BY
bg_BG
ca_ES
cs_CZ
da_DK
de_DE
396LW NO topic_id
AD
Další témata ....(Topics)
Converting to string: TypedValue{t=0x10/d=0xe a=-1}
- 14
// error
- "18"
// ok
Chytré telefony s Androidem - tabulka srovnání dle ceny:
|
Výrobce |
Model (codename) |
Cena, včetně DPH |
CPU MHz |
displej-rozlišení |
Velikost displeje v palcích |
ROM |
RAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Huawei |
Vodafone 845 (U8120, Joy) |
1979 |
528 |
240x320 |
2.8 |
512 |
256 |
|
ZTE |
Vodafone 945 (ZTE Joe) |
1999 |
600 |
240x400 |
3.2 |
512 |
512 |
|
Huawei |
Vodafone 858 Smart (U8160) |
2177 |
528 |
240x320 |
2.8 |
512 |
256 |
|
Alcatel |
T-Mobile Move (OT 908) |
2294 |
600 |
240x320 |
2.8 |
512 |
512 |
|
Samsung |
Galaxy Y (S5360) |
2495 |
832 |
240x320 |
3 |
512 |
256 |
|
ZTE |
Racer II (Arizona) |
2536 |
500 |
240x320 |
2.8 |
512 |
256 |
|
Huawei |
Ideos X1 (U8180, Orange Stockholm) |
2549 |
528 |
240x320 |
2.8 |
512 |
256 |
|
Huawei |
U8100 |
2595 |
528 |
240x320 |
2.8 |
512 |
256 |
|
Huawei |
U8500 |
2699 |
600 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
512 |
256 |
|
Samsung |
Galaxy Mini (S5570) |
2799 |
600 |
240x320 |
3.14 |
512 |
256 |
|
Samsung |
Galaxy 5, 550 (i5500) |
2855 |
600 |
240x320 |
2.8 |
512 |
256 |
|
LG |
Optimus Me (P350) |
2924 |
600 |
240x320 |
2.8 |
512 |
512 |
|
SE |
Xperia X8 |
2977 |
600 |
320x480 |
3 |
512 |
256 |
|
Gigabyte |
GSmart G1310 (Roy) |
2990 |
528 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
512 |
256 |
|
MyPhone |
A210 |
2990 |
624 |
240x400 |
3 |
256 |
128 |
|
ZTE |
Orange San Francisco (ZTE Blade, U880, P729V) |
2999 |
600 |
480x800 |
3.5 |
512 |
512 |
|
HTC |
Explorer (Pico) |
3104 |
600 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
512 |
512 |
|
Huawei |
U8650 (Sonic) |
3290 |
600 |
320x480 |
3.5 |
512 |
256 |
|
Huawei |
Ideos X3 (U8510, Blaze) |
3377 |
600 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
512 |
256 |
|
Samsung |
Galaxy Y Pro (B5510) |
3390 |
832 |
240x320 |
2.6 |
|
|
|
Gigabyte |
GSmart G1317D (Rola) |
3504 |
528 |
240x400 |
3.2 |
512 |
256 |
|
SE |
Xperia Live Walkman (WT19i) |
3554 |
1000 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
1024 |
512 |
|
Huawei |
T-Mobile Comet (Ideos, U8150) |
3600 |
528 |
240x320 |
2.8 |
512 |
256 |
|
SE |
Xperia X10 mini pro (U20i, Mimmi) |
3777 |
600 |
240x320 |
2.55 |
512 |
256 |
|
LG |
Optimus Swift (GT540) |
3800 |
600 |
320x480 |
3 |
512 |
256 |
|
SE |
Xperia Mini (ST15) |
3800 |
1000 |
320x480 |
3 |
1024 |
512 |
|
LG |
Optimus One (P500) |
3919 |
600 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
512 |
512 |
|
LG |
Optimus Pro |
3928 |
800 |
240x320 |
2.8 |
512 |
256 |
|
HTC |
Wildfire (Buzz, Mocha, A3333) |
3999 |
528 |
240x320 |
3.2 |
512 |
384 |
|
LG |
Optimus Net (P690) |
4108 |
800 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
512 |
512 |
|
Samsung |
Galaxy Gio (S5660) |
4185 |
800 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
512 |
384 |
|
LG |
Optimus Hub (Univa) |
4195 |
800 |
320x480 |
3.5 |
512 |
512 |
|
SE |
Xperia X10 mini (E10i, Robyn) |
4195 |
600 |
240x320 |
2.55 |
512 |
256 |
|
Samsung |
Galaxy 3, 580, Taos (i5800) |
4500 |
667 |
240x400 |
3.2 |
512 |
256 |
|
Samsung |
Galaxy Ace+ (S7500) |
4550 |
1000 |
320x480 |
3.65 |
4096 |
512 |
|
LG |
Optimus Chic (E720) |
4550 |
600 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
512 |
512 |
|
Samsung |
Galaxy 551 (i5510) |
4577 |
667 |
240x400 |
3.2 |
512 |
512 |
|
Motrolola |
Liquid Mini E310 |
4600 |
600 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
512 |
512 |
|
HTC |
Wildfire S (Marvell) |
4777 |
600 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
512 |
512 |
|
Verzo |
Kinzo |
4799 |
1000 |
480x800 |
4.3 |
512 |
512 |
|
Samsung |
Galaxy Ace (S5830) |
4800 |
800 |
320x480 |
3.5 |
512 |
256 |
|
Motorola |
Defy mini |
4800 |
600 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
512 |
512 |
|
Samsung |
Galaxy Spica, Portal, Lite (i5700) |
4800 |
800 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
512 |
256 |
|
HTC |
Gratia (A6380, Liberty, Aria) |
4937 |
480 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
512 |
384 |
|
SE |
Xperia mini pro (SK17i, Mango) |
4944 |
1000 |
320x480 |
3 |
1024 |
320 |
|
Huawei |
Ideos X5 (U8800) |
4977 |
800 |
480x800 |
3.8 |
4096 |
512 |
|
HTC |
Salsa (C510e) |
4990 |
600 |
320x480 |
3.4 |
576 |
512 |
|
Huawei |
Boulder |
4998 |
528 |
240x320 |
2.6 |
512 |
256 |
|
ZTE |
Orange Monte Carlo (ZTE Skate) |
5177 |
800 |
480x800 |
4.3 |
512 |
512 |
|
Samsung |
Galaxy S (i9000) |
5300 |
1000 |
480x800 |
4 |
15600 |
512 |
|
Gigabyte |
GSmart G1315 |
5490 |
528 |
320x480 |
3.5 |
512 |
256 |
|
SE |
Xperia Active |
5500 |
1000 |
320x480 |
3 |
1024 |
512 |
|
Samsung |
Google Nexus One |
5750 |
1000 |
480x800 |
3.7 |
512 |
512 |
|
HTC |
Desire (A8181, Bravo) |
5999 |
1000 |
480x800 |
3.7 |
576 |
512 |
|
LG |
Optimus Black (P970) |
6000 |
1000 |
480x800 |
4 |
1908 |
512 |
|
SE |
Xperia Play |
6000 |
1000 |
480x854 |
4 |
|
|
|
LG |
Optimus Sol (Victor, E730) |
6000 |
1000 |
480x800 |
3.8 |
2048 |
512 |
|
Acer |
Liquid Metal S120 |
6061 |
800 |
480x800 |
3.6 |
512 |
512 |
|
Samsung |
Google Nexus S |
6200 |
1000 |
480x800 |
4 |
15600 |
512 |
|
HTC |
Desire Z (A7272, Vision) |
6200 |
800 |
480x800 |
3.7 |
1536 |
512 |
|
Samsung |
Galaxy W (i8150, Ancora) |
6200 |
1400 |
480x800 |
3.7 |
4096 |
512 |
|
SE |
Xperia Ray (ST18i) |
6344 |
1000 |
480x854 |
3.3 |
1024 |
512 |
|
Motorola |
Defy (MB525, Jordan) |
6377 |
800 |
480x854 |
3.7 |
1908 |
512 |
|
Motorola |
Defy + (MB526) |
6377 |
1000 |
480x854 |
3.7 |
1908 |
512 |
|
Samsung |
Galaxy XCover (S5690) |
6399 |
800 |
320x480 |
3.65 |
512 |
512 |
|
Gigabyte |
GSmart G1345 |
6490 |
800 |
320x480 |
3.5 |
512 |
512 |
|
HTC |
Evo 3D |
6500 |
1200 |
540x960 |
4.3 |
1024 |
1024 |
|
HTC |
Desire HD (Ace) |
6500 |
1000 |
480x800 |
4.3 |
1900 |
768 |
|
Huawei |
Honour (U8660) |
6500 |
1400 |
480x854 |
4 |
4096 |
512 |
|
SE |
Xperia Neo |
6590 |
1000 |
480x854 |
3.7 |
1024 |
512 |
|
HTC |
Legend (A6363) |
6784 |
600 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
512 |
384 |
|
Huawei |
Vision (U8850) |
6999 |
1000 |
480x800 |
3.7 |
2048 |
512 |
|
SE |
Xperia Arc (LT15i) |
7390 |
1000 |
480x854 |
4.2 |
1024 |
512 |
|
SE |
Xperia Pro (MK16i) |
7890 |
1000 |
480x854 |
3.7 |
1024 |
512 |
|
HTC |
Hero |
7975 |
528 |
320x480 |
3.2 |
288 |
512 |
|
SE |
Xperia Arc S (LT18i) |
8590 |
1400 |
480x854 |
4.2 |
1024 |
512 |
|
Samsung |
Xperia Live Walkman (WT19i) |
9700 |
1500 |
480x800 |
4.3 |
16000 |
1024 |
|
Motorola |
Droid Razr |
11800 |
1200 |
540x960 |
4.3 |
15600 |
1024 |
Issue:
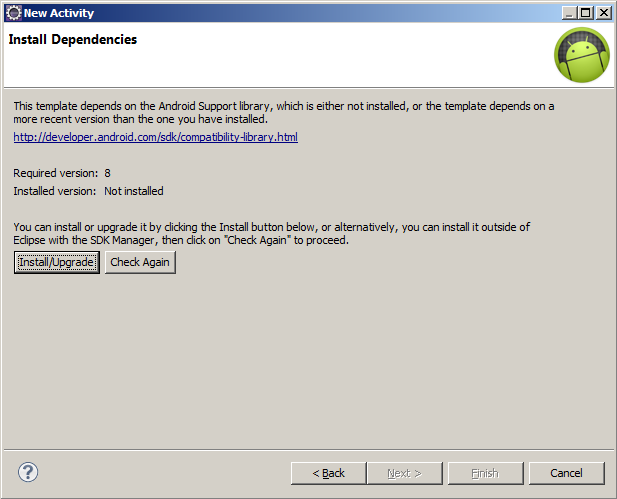
When using New Activity wizard, ADT 20 asked to install Android Support library version 8 even though version 9 has been installed.
Pressing "Install/Update" then ADT popup a window downloading Support library, when finished nothing happen.
Pressing "Check Again" does nothing.
If i restarting Eclipse again this problem.
Notice: If you install new version ADT or update via SDK Manager, open SDK Manager standalone and close Eclipse.
Workaround:
- Close Eclipse
- Open SDK Manager standalone (c:\Program Files\Android\android-sdk-windows\SDK Manager.exe)
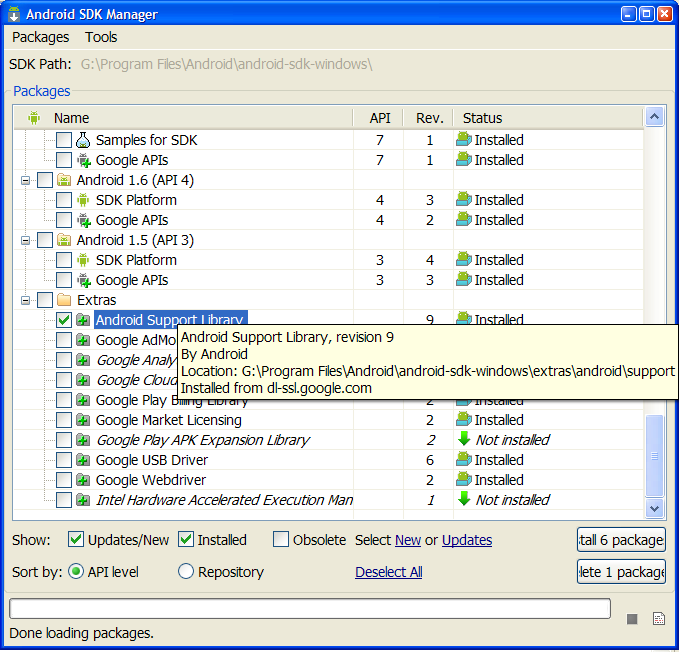
- Check the checkbox and uninstall Extras -> Android Support Library.
- Check again Extras -> Android Support Library and install it
- Restart Eclipse
- Try to create new project
When using New Activity wizard, ADT 20 asked to install Android Support library version 8 even though version 9 has been installed.
Pressing "Install/Update" then ADT popup a window downloading Support library, when finished nothing happen.
Pressing "Check Again" does nothing.
If i restarting Eclipse again this problem.
Notice: If you install new version ADT or update via SDK Manager, open SDK Manager standalone and close Eclipse.
Workaround:
- Close Eclipse
- Open SDK Manager standalone (c:\Program Files\Android\android-sdk-windows\SDK Manager.exe)
- Check the checkbox and uninstall Extras -> Android Support Library.
- Check again Extras -> Android Support Library and install it
- Restart Eclipse
- Try to create new project


MainActivity.java
activity_main.xml
AndroidManifest.xml do not forget INTERNET uses-permission !!!!!!!
package com.asynctaskexample;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpClient;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ProgressBar;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private TextView textView;
private ProgressBar progressBar;
private DownloadWebPageTask mTask = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.TextView01);
downloadPage();
}
// AsyncTask <TypeOfVarArgParams , ProgressValue , ResultValue> .
private class DownloadWebPageTask extends AsyncTask<String, Integer, String> {
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
//textView.setText("Hello !!!");
progressBar = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.progressBar1);
progressBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
super.onPreExecute();
}
@Override
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... values) {
super.onProgressUpdate(values);
}
@Override
protected String doInBackground(String... urls) {
String response = "";
for (String url : urls) {
DefaultHttpClient client = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(url);
try {
HttpResponse execute = client.execute(httpGet);
InputStream content = execute.getEntity().getContent();
BufferedReader buffer = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
content));
String s = "";
while ((s = buffer.readLine()) != null) {
response += s;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return response;
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String result) {
progressBar.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
textView.setText(result);
}
}
private void downloadPage() {
if (mTask != null
&& mTask.getStatus() != DownloadWebPageTask.Status.FINISHED) {
mTask.cancel(true);
}
// execute(String[]) you can put array of links to web pages, or array of Integer[]
// if first param is Integer[] etc.
mTask = (DownloadWebPageTask) new DownloadWebPageTask()
.execute(new String[] { "//android.okhelp.cz/android-market.html",
"//android.okhelp.cz/android-market.html" });
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
if (mTask != null
&& mTask.getStatus() != DownloadWebPageTask.Status.FINISHED) {
mTask.cancel(true);
mTask = null;
}
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_main, menu);
return true;
}
}
activity_main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="//schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressBar1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/TextView01"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
</LinearLayout>
AndroidManifest.xml do not forget INTERNET uses-permission !!!!!!!
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
Windows 7 64-bit version.
Eclipse 64-bit - Java was started but returned exit code=13
Solution:
Download and install 64-bit version of JDK
//www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk7-downloads-1880260.html
Eclipse 64-bit - Java was started but returned exit code=13
Solution:
Download and install 64-bit version of JDK
//www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk7-downloads-1880260.html
Editace: 2013-11-10 22:00:41
Počet článků v kategorii: 396
Url:tolowercase-locale-toupercase-locale-java-android



