Get Context Java Android example
getContext() getApplicationContext() method Java Android example source
Context myContext_1 = ThisClassName.this; // to open a Dialog
Context myContext_2 = getContext();
Context myContext_3 = this.getContext();
Context myContext_4 = this;
Context myContext_5 = this.getApplicationContext ();
OnClickListener getImageBtnOnClick = new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View view) {
Context context = view.getContext();
}
};
// Toast
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Context == getApplicationContext "
, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// store Context in public class
public class MyActivity extends Activity {
public static Context myCnt = null;
...
protected void onCreate(Bundle icicle) {
...
myCnt = this;
MyStorage.setContext(myCnt);
// or
// MyStorage.setContext(this);
// cntxFromStorage == this
Context cntxFromStorage = MyStorage.getContext();
...
};
};
public class MyStorage
{
private static Context cntStorageContext = null;
public static Context getContext() {
return cntStorageContext;
}
public static void setContext(Context context) {
MyStorage.cntStorageContext = context;
}
};
class DataBaseHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
// get MyActivity context
Context cnt = MyStorage.getContext();
}
396LW NO topic_id
AD
Další témata ....(Topics)
Try this solution:
AdView adView = new AdView(getApplicationContext());//in menu inflater getActivity()
adView.setAdUnitId("ca-app-pub-87***yourNumber");
adView.setAdSize(AdSize.BANNER);
LinearLayout linLay = (LinearLayout)findViewById(R.id.idReklamaLayout);
// Add the adView to it
linLay.addView(adView);
// Initiate a generic request to load it with an ad
if(Build.MANUFACTURER.equals("unknown")) {
// Emulator
AdRequest.Builder.addTestDevice("B3EEABB8EE11C2BE770B684D95219ECB"); // to get test ads on this device.
AdRequest adRequest = new AdRequest.Builder()
.addTestDevice(AdRequest.DEVICE_ID_EMULATOR) // All emulators
.addTestDevice("B3EEABB8EE11C2BE770B684D95219ECB") // Emulator id you will get in the LogCat verbose
.build();
adView.loadAd(adRequest);
/* */
}else {
// Not Emulator
// Initiate a generic request to load it with an ad
AdRequest adRequest = new AdRequest.Builder().build();
adView.loadAd(adRequest);/**/
}
- File->Project Structure Ctrl + Alt + Shift + S
- Select module and Dependencies Tab
- Click on + PLUS button (right upper corner)
- Select library
Click OK, OK
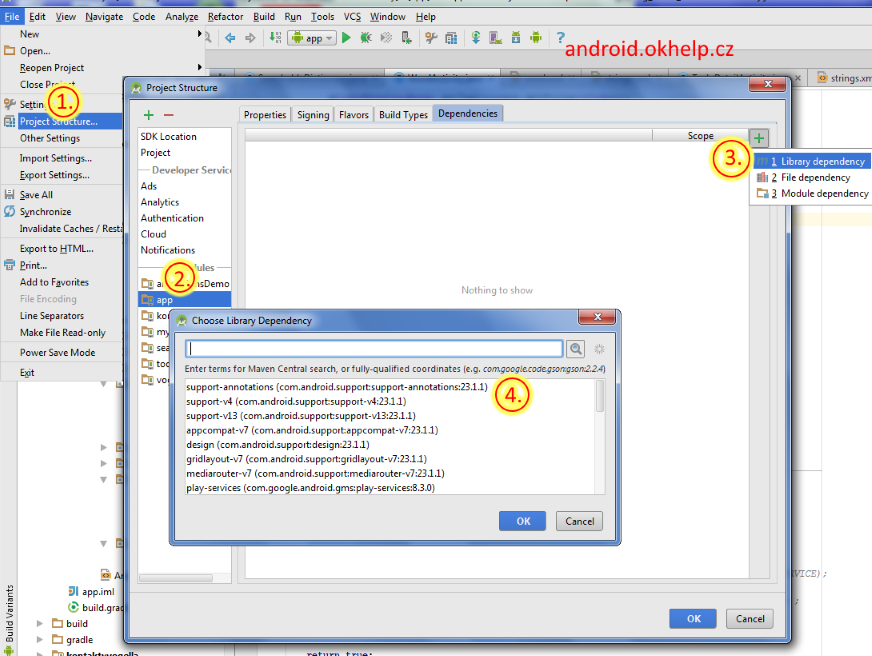
If I trying
android-sdk_r22.6.2-windows.zip
adt-bundle-windows-x86_64-20140321.zip
and open xml layout graphic editor and xml layout file
memory continues to grow to crashes Eclipse
https://developer.android.com/sdk/index.html
I have to install old version adt-bundle-windows-x86-20131030.zip
what working fine.
I had to delete .metadata folder in workspace if I want open old version ADT
android-sdk_r22.6.2-windows.zip
adt-bundle-windows-x86_64-20140321.zip
and open xml layout graphic editor and xml layout file
memory continues to grow to crashes Eclipse
https://developer.android.com/sdk/index.html
I have to install old version adt-bundle-windows-x86-20131030.zip
what working fine.
I had to delete .metadata folder in workspace if I want open old version ADT
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(new SampleView(this));
}
private static class SampleView extends View {
// CONSTRUCTOR
public SampleView(Context context) {
super(context);
setFocusable(true);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
//drawARGB (int a, int r, int g, int b)
// a alpha component (0..255) of the color to draw onto the canvas
// r red component (0..255)
// g green component (0..255)
// b blue component (0..255)
canvas.drawARGB(255, 0, 255, 10);
}
}
}
If I create own folder layout-w320dp with Eclipse Android 4.4
layout was correctly loaded.
If I trying this application on tablet with Android 2.1 application crashed.
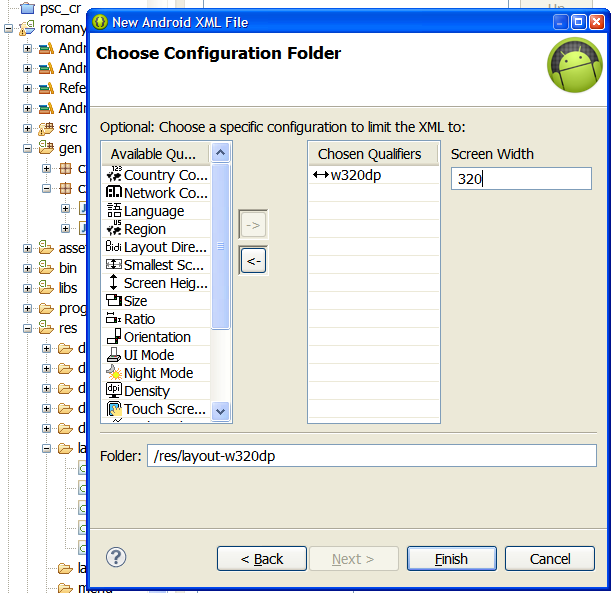
layout was correctly loaded.
If I trying this application on tablet with Android 2.1 application crashed.

Editace: 2011-10-15 08:31:19
Počet článků v kategorii: 396
Url:get-context-java-android-example



