Convert Activity to Fragment Step by Step
public class Main extends Activity {
private TextView mTextView;
private Activity mAct;
private Intent mIntent;
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main_layout);
mTextView = findViewById(R.id.mTextView);
mAct = getActivity();
mIntent = getIntent();
}
}
to:
public class Main extends Fragment{
private TextView mTextView;
private FragmentActivity mFrgAct;
private Intent mIntent;
private LinearLayout mLinearLayout;
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View root = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_main, null);
return root;
}
public void onViewCreated(View view, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// you can add listener of elements here
/*Button mButton = (Button) view.findViewById(R.id.button);
mButton.setOnClickListener(this); */
mTextView = view.findViewById(R.id.mTextView);
mLinearLayout = (LinearLayout)view;
}
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
mFrgAct = getActivity();
mIntent = mFrgAct.getIntent(); // Intent intent = new Intent(getActivity().getIntent());
}
}
396LW NO topic_id
AD
Další témata ....(Topics)
If you change the package name, you have to add new package name in:
DictionaryProvider.java
Do not forget change package name in all java class and xml/searchable.xml
In my project I changed like this:
DictionaryProvider.java
public class DictionaryProvider extends ContentProvider {
String TAG = "DictionaryProvider";
// public static String AUTHORITY = "com.example.android.searchabledict.DictionaryProvider";
// change to your new package name
public static String AUTHORITY = "com.myweb.mysubdomen.searchabledict.DictionaryProvider";
public static final Uri CONTENT_URI = Uri.parse("content://" + AUTHORITY + "/dictionary");
// in AndroidManifest.xml
//change com.example.android to your package e.g. com.myweb.mysubdomen
<!-- Provides search suggestions for words and their definitions. -->
<provider android:name="com.example.android.searchabledict.DictionaryProvider"
android:configChanges="keyboard|keyboardHidden|orientation"
android:authorities="com.example.android.searchabledict.DictionaryProvider" />
<!-- Points to searchable activity so the whole app can invoke search. -->
<meta-data android:name="android.app.default_searchable"
android:configChanges="keyboard|keyboardHidden|orientation"
android:value=".SearchableDictionary" />
// I change like this:
<!-- Provides search suggestions for words and their definitions. -->
<provider android:name=".DictionaryProvider"
android:configChanges="keyboard|keyboardHidden|orientation"
android:authorities="cz.okhelp.android.searchabledict.DictionaryProvider" />
<!-- Points to searchable activity so the whole app can invoke search. -->
<meta-data android:name="android.app.default_searchable"
android:configChanges="keyboard|keyboardHidden|orientation"
android:value=".SearchableDictionary" />
Do not forget change package name in all java class and xml/searchable.xml
In my project I changed like this:
<searchable xmlns:android="//schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:label="@string/search_label"
android:hint="@string/search_hint"
android:searchSettingsDescription="@string/settings_description"
android:searchSuggestAuthority="cz.okhelp.android.searchabledict.DictionaryProvider"
android:searchSuggestIntentAction="android.intent.action.VIEW"
android:searchSuggestIntentData="content://cz.okhelp.android.searchabledict.DictionaryProvider/dictionary"
android:searchSuggestSelection=" ?"
android:searchSuggestThreshold="1"
android:includeInGlobalSearch="true"
>
</searchable>
On Android device is path to *.apk like this example:
How get package *.apk path on device dynamically Android example
/data/app/cz.okhelp.my_package.apkHow get package *.apk path on device dynamically Android example
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
String sPackagePath = getPackageResourcePath();
}
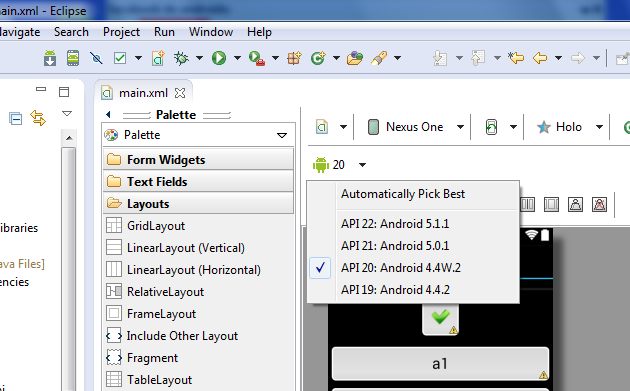
Click to Android version combobox - drop down menu and select your version, which just using (have instaled). For example: You updated ADT by SDK manager, but forget to update Android version. You can use lower version from drop down menu, which using your project, or do update of Android by SDK manager.

private SensorManager mSensorManager;
private PowerManager mPowerManager;
private WindowManager mWindowManager;
private Display mDisplay;
// onCreate
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Get an instance of the SensorManager
mSensorManager = (SensorManager) getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE);
// Get an instance of the PowerManager
mPowerManager = (PowerManager) getSystemService(POWER_SERVICE);
// Get an instance of the WindowManager
mWindowManager = (WindowManager) getSystemService(WINDOW_SERVICE);
mDisplay = mWindowManager.getDefaultDisplay();
setContentView(R.layout.main); // main.xml or your xml file name
}
If You have old PC (Android in emulator with high screen resolution uses a lot of memory) or your testing phone have small screen, You can try this trick.
Rename layout folder for small device screen f.g. from layout into layout-swXXXdp and a large layout-sw600dp into layout.
Your phone with small screnn will do select xml file from renamed layout folder (for small screen).
You can to testing rotation with device en stability of fragments if an application changed orientation.
If you have old pc, you can try to make a new virtual device running on older version of Android, which uses less memory of computer.
For testing of rotation stability - application orientation changed - use on emulator Ctrl+F11, Ctrl+F12 key (Windows).
Important
Before the release of application, you have to rename layout folder to older name layout-sw600dp and layout-swXXXdp to layout.
Rename layout folder for small device screen f.g. from layout into layout-swXXXdp and a large layout-sw600dp into layout.
Your phone with small screnn will do select xml file from renamed layout folder (for small screen).
You can to testing rotation with device en stability of fragments if an application changed orientation.
If you have old pc, you can try to make a new virtual device running on older version of Android, which uses less memory of computer.
For testing of rotation stability - application orientation changed - use on emulator Ctrl+F11, Ctrl+F12 key (Windows).
Important
Before the release of application, you have to rename layout folder to older name layout-sw600dp and layout-swXXXdp to layout.
Editace: 2017-02-04 17:50:34
Počet článků v kategorii: 396
Url:convert-activity-to-fragment-step-by-step



