How set gray text to EditText Android example
Example source code for Android development. How set gray text to EditText when EditText is blank.
Hint text to display when the text is empty.
In layout/main.xml insert to EditText row Attribute Name android:hint="Some text"
Programatically you can use method setHint:
Hint text to display when the text is empty.
In layout/main.xml insert to EditText row Attribute Name android:hint="Some text"
<EditText
android:id="@+id/myEdit"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:hint="Some text"
android:singleLine="true"
</EditText>
Programatically you can use method setHint:
// setHint(CharSequence hint) example
(EditText)findViewById(R.id.myEdit).setHint("My text");
// or int resId as method setHint(int resId)
EditText myEdit = findViewById(R.id.myEdit);
myEdit.setHint(R.string.app_name);
396LW NO topic_id
AD
Další témata ....(Topics)
Eclipse: failed to create the java virtual machine - message box
- Open folder with Eclipse.exe and find eclipse.ini file
- Replace -vmargs
by your current real path of javaw.exe:
-vm "c:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.7.0_07\bin\javaw.exe"
-startup
plugins/org.eclipse.equinox.launcher_1.3.0.v20120522-1813.jar
--launcher.library
plugins/org.eclipse.equinox.launcher.win32.win32.x86_1.1.200.v20120522-1813
-product
com.android.ide.eclipse.adt.package.product
--launcher.XXMaxPermSize
256M
-showsplash
com.android.ide.eclipse.adt.package.product
--launcher.XXMaxPermSize
256m
--launcher.defaultAction
openFile
-vm "c:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.7.0_07\bin\javaw.exe”
-Dosgi.requiredJavaVersion=1.6
-Xms40m
-Xmx768m
-Declipse.buildId=v21.1.0-569685
ACRA allows your Android application to send Crash Reports to various destinations:
a Google Docs spreadsheet (default and original behavior)
an email
your own server-side HTTP POST script
any other possible destination by implementing your own report sender
ACRA wiki and download page of project library
a Google Docs spreadsheet (default and original behavior)
an email
your own server-side HTTP POST script
any other possible destination by implementing your own report sender
ACRA wiki and download page of project library
public boolean isConnected() {
try {
ConnectivityManager cm = (ConnectivityManager) getSystemService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);
return cm.getActiveNetworkInfo().isConnectedOrConnecting();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
Log.e("isConnected", e.getMessage());
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), e.getMessage(),
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return false;
}
This version of the rendering library is more recent than your version of ADT plug-in. Please update ADT plug-in
Click on menu Help > Install New Software.
In the Work with field, Add: https://dl-ssl.google.com/android/eclipse/
Select: Developer Tools / Android Development Tools.
Click Next to complete the wizard.
If you have problem try download all sdk + eclipse in one pack , rename old folder for example Andorid_old, create new folder Android and unpack sdk + eclipse from this adress:
//developer.android.com/sdk/index.html
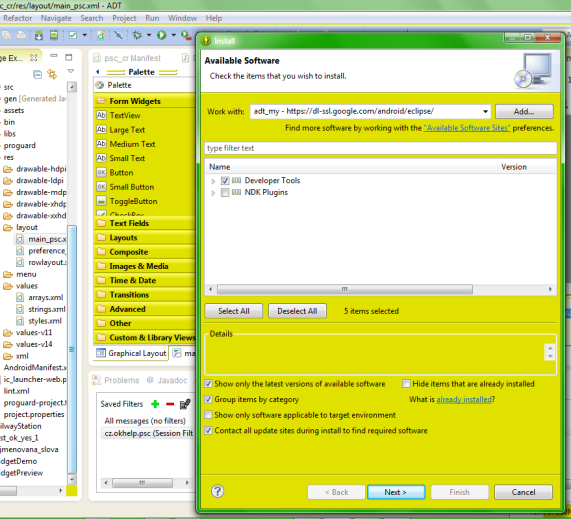
Click on menu Help > Install New Software.
In the Work with field, Add: https://dl-ssl.google.com/android/eclipse/
Select: Developer Tools / Android Development Tools.
Click Next to complete the wizard.
If you have problem try download all sdk + eclipse in one pack , rename old folder for example Andorid_old, create new folder Android and unpack sdk + eclipse from this adress:
//developer.android.com/sdk/index.html

ScrollTo(), getTop(), getBottom(), getLeft(), getRight(), ScrollView, LinearLayout Android Java xml example.
How get position of a View.
MainClass.java
main.xml
How get position of a View.
MainClass.java
/*
public void scrollTo (int x, int y)
Since: API Level 1
Set the scrolled position of your view. This will cause a call to onScrollChanged(int, int, int, int) and the view will be invalidated.
This version also clamps the scrolling to the bounds of our child.
Parameters
x the x position to scroll to
y the y position to scroll to
*/
// sroll to top of hscrollViewMain
ScrollView hscrollViewMain = (ScrollView)findViewById(R.id.scrollViewMain);
hscrollViewMain.scrollTo(0, 0); // scroll to application top
// get position of a View
EditText hEdit = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.username_edit);
int nY_Pos = hEdit.getTop(); // getBottom(); X_pos getLeft(); getRight();
// scroll to top of hEdit
hscrollViewMain.scrollTo(0,nY_Pos);
main.xml
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="//schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ScrollView
android:id="@*id/scrollViewMain"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="0dip"
android:layout_weight="1">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingTop="5dip"
android:paddingBottom="13dip"
android:paddingLeft="20dip"
android:paddingRight="20dip">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/message"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceSmall"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="5dip" />
<TextView
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceSmall"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/login_activity_username_label" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/username_edit"
android:singleLine="true"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:minWidth="250dip"
android:scrollHorizontally="true"
android:capitalize="none"
android:autoText="false"
android:inputType="textEmailAddress" />
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
</LinearLayout>
Editace: 2011-09-26 20:49:01
Počet článků v kategorii: 396
Url:how-set-gray-text-to-edittext-android-example



